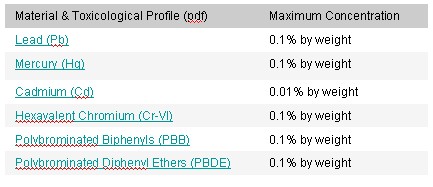
REACH

ASTM D2000 was introduced to provide engineers with a classification system for commercially available rubber materials and to provide a simple designation method called the “Line call-out.” Although the title specifies automotive application it is not limited to only the automotive industry. In fact several industries benefit from this standard.
The most common material classification system used in rubber parts specification is probably “Standard Classification System for Rubber Products in Automotive Applications.” or ASTM D 2000. This system is designed to aid in the selection of practical rubber products for specific environments and provides a “line call-out” designation for the specification of elastomer seal materials.
How to read an ASTM D 2000/ SAE J200 Line Call-Out
Specification Revision
| ASTM D2000-99 | M | 2 | HK | 7 | 14 | A1-10, B38, C12, EF31, EO88, F15, Z1 |
This indicates the revision year of D2000 to which the line call-out makes reference.
Measurement Units
| ASTM D2000-99 | M | 2 | HK | 7 | 08 | A1-10, B38, C12, EF31, EO88, F15, Z1 |
If an M is present, metric units will be used for tensile strength, temperature, and tear strength (MPa, °C, and kN/m respectively). If no M is present, English units will be used (psi, °F, and ppi respectively).
Grade Number
ASTM D2000-99M2HK708A1-10, B38, C12, EF31, EO88, F15, Z1
Indicates the level of test requirements to which a material may be subjected. For example, Grade 1 shows that only basic properties are required, while Grades 2-9 require additional testing criteria such as low temperature brittleness or special heat aging tests. In our example, we will be looking at a fluorocarbon material that must meet some or all Grade 2 requirements. Note that Grade Numbers may not be relevant to all material Types and Classes.
Type and Class
ASTM D2000-99M2HK708A1-10, B38, C12, EF31, EO88, F15, Z1
“HK” – The first letter, “H”, is the designation for Type (resistance to heat aging) as shown in table 1. The second letter, “K”, is the designation for Class (resistance to swelling in oil) as shown in Table 2.
| Type | Test Temperature |
| A | 70°C (158°F) |
| B | 100°C (212°F) |
| C | 125°C (257°F) |
| D | 150°C (302°F) |
| E | 175°C (347°F) |
| F | 200°C (392°F) |
| G | 225°C (437°F) |
| H | 250°C (482°F) |
| J | 275°C (527°F) |
Table 1
| Class | Volume Swell, max |
| A | no requirement |
| B | 140% |
| C | 120% |
| D | 100% |
| E | 80% |
| F | 60% |
| G | 40% |
| H | 30% |
| J | 20% |
| K | 10% |
Table 2, Tested for 70 hrs @ temperature from
table 1 in ASTM Oil No 3.
The table shown below are the most common polymers used for type and class. Classification System D 2000 SAE J200 Material Designation (Type and Class)
| Type of Polymer most often used | |
| AA | Natural rubber, reclaimed rubber, SBR, butyl, EP polybutadiene, polyisoprene |
| AK | Polysulfides |
| BA | Ethylene propylene, high temperature SBR, butyl compounds |
| BC | Chloroprene polymers (neoprene), cm |
| BE | Chloroprene polymers (neoprene), cm |
| BF | NBR polymers |
| BG | NBR polymers, urethanes |
| BK | NBR |
| CA | Ethylene propylene |
| CE | Chlorosulfinated polyethylene (Hypalon), cm |
| CH | NBR polymers, epichlorohydrin polymer |
| DA | Ethylene propylene polymers |
| DE | CM, CSM |
| DF | Polyacrylic (butyl-acrylate type) |
| DH | Polyacrylic polymers, HNBR |
| EE | AEM |
| EH | ACM |
| EK | FZ |
| FC | Silicone (high strength) |
| FE | Silicones |
| FK | Fluorinated silicones |
| GE | Silicones |
| HK | Fluorinated elastomers (Vito, Fluorel, etc.) |
| KK | Perfluoroelastomers |
For each Type and Class, ASTM D 2000 includes a table giving all basic requirements, physical properties, and all suffix requirements.
| Hardness (Durometer) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| This number indicates durometer range in Shore A units (plus or minus 5 points). In our example, the material specified would possess a hardness of 70±5 durometer. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Tensile Strength | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| The next two digits indicate the material’s minimum tensile strength. If measurements are in metric units, the digits show MPa. If measurements are in English units, the digits show psi and only the first two digits of that measurement are indicated. In our example (which is in metric units), the two tensile strength digits are “14” thus the minimum tensile strength required would be 14MPa. If this example were non-metric, this callout would be 20 (14 Mpa = 2031 psi).
The first six characters of a Line Call-Out give a lot of basic information about the type of elastomer required and its physical properties. Most specifications require more information to guarantee that the seal will meet the needs of the application. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Additional Requirement Suffixes | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Suffixes appended to the Line Call-Out are letter and number combinations that indicate a material’s test and performance criteria per the Grade number indicated. In our example, A1-10 indicates a heat resistance test. B38 indicates a compression set test. C12 indicates resistance to ozone. EF31 and EO88 indicate fluid resistance criteria. F15 indicates low temperature brittleness criteria. Z1 indicates a user-defined requiremen, t as must be specified including test criteria. Refer to ASTM D 2000 for expanded suffix call-out details. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Our support Hotline is available 12 Hours a day.
Tel: +86-319-8032 626
Email: shida@shidarubber.com
Looking forward to receiving your inquiries!
IATF 16949: 2016 certified manufacturer with 20 years of experience.
China Manufacturer, Supplier, Factory of Extruded EPDM Rubber Profiles, Cellular EPDM Rubber Profiles, Self-gripping Gaskets, Sponge Rubber Seals, Edge Protectors and Sealing Sections.
Test reports / datasheets are available.

